A mirror image of racial tensions from the 1920s and today in the Peace Garden State
Alt-White: The Siege of North Dakota. Part Three in the series on racism in North Dakota. Inescapable comparisons between the political, racial, and economic sectors of the 1920s and 2010s. Local resident hunts Fargo’s Nazis, posts alert advertisements around Fargo.
By C.S. Hagen
FARGO – The day North Dakota women marched on Bismarck, a lone vehicle flying a Confederate flag cruised down Broadway, according to Fargo emergency dispatch. The pickup truck was stopped at Fourth Avenue when a middle-aged man jumped onto the back and attempted to take the Stars and Bars away.
A fight between three white males ensued. Police responded, but late; all parties had already fled, according to Fargo Police Department Deputy Chief Jospeh Anderson.
“A car drove by and a male took the flag off the car and tried to run, comp [Pete Tefft] confronted him about it and he tried to fight him,” dispatch personnel reported.
Tefft, who has been anonymously identified as a Fargo Nazi in alert posters stapled to telephone poles around the Downtown area, decided to stop the flag-stealing assailant, according to dispatch personnel reports. Tefft called 911 at 12:13 p.m., January 21, 2017.
Tefft made reference to the incident in a letter he wrote pertaining to the Women’s March on the InForum on January 30. He explained the women’s march was more of an anti-Trump march, and anyone with differing ideologies was shunned. “From muttering curse words and insults like ‘white-supremacist’ at anyone holding even a subtle pro-life banner to a deranged middle-aged man stealing a confederate flag from three jovial teenage counter-protesters, participants did nothing and sometimes were complacent to the point of accessory to what could be categorized as terrorism.
“Stealing someone’s property, a child’s, because they have an opposing political ideology is not an argument but an admission you lost the argument. Everybody that stood by, watched, or attempted to thwart actions to stop the theft, participants and store owners alike, should be ashamed of themselves.”
In Facebook posts Tefft’s political views were made clearer. “I’d oppress anyone that wants to stop me from preserving my race and culture, wouldn’t you?” Tefft wrote in a January 29 Facebook debate.
Soon after the Confederate flag incident, Moorhead resident Luke Safely started putting up alert posters throughout town naming Tefft a Nazi. He found out about the incident on Broadway, and began research, which led to him naming Tefft a “super Nazi racist.
“I told Tefft if you want to go out and practice your culture, then go out and practice your culture,” Safely said. “But don’t oppress other cultures. I hope that when people see all this information, and see Pete Tefft for who he is, they can see other people in the community.”

Luke Safely talking about his decision to publicize what he says is a Fargo Nazi – photo by C.S. Hagen
He first shared the information online, but the “liberal bubble” was not enough. “I thought maybe the community should know.” He alerted Tefft to his intentions, to which Tefft said he defended himself by saying he was merely pro-white.
Some of Safely’s friends say that the exposure is simply spreading Nazi rhetoric, which will help the likeminded solidify. “But right now, that rhetoric is mainstream,” Safely said. “Look at Breitbart, look at Steve Bannon, the rhetoric is already out there, and the funny thing is we don’t admit that it has spread.
“That’s willful ignorance, and it’s North Dakota nice.”
Other friends think that since no physical violence has been initiated by white supremacists, he should wait.
Racism, Safely said, creates emotional and social violence, which leads to physical violence.
“By not telling someone what they’re doing is wrong, you’re pretty much telling them that what they’re doing is right.”
There are other verbose white supremacists in the Fargo Moorhead area, Safely said. So far, he’s watching three who claim to be Nazis and have online presences. He’s also not afraid of a civil lawsuit, Safely said, because the evidence behind his claim is overwhelming.
“I get that people are scared,” Safely said. “The Christians are scared, the Muslims are scared, everyone is scared. I get that the Muslim ban makes people feel safe, but it’s only replying to our fear with more hatred.”
Tefft refused to comment saying only, “I’ve been consulted by my church elders to not speak with you.”
Safely has been threatened by one person online, he said. “I realize that by doing this and by putting my face on it that I was totally going to put myself in a situation of danger, because outing a Nazi like that a lot of other Nazis are going to be scared about it. The thing I realized is that a lot of the direct action against Nazis these days are done anonymously. We need to start putting our faces to it. These “alt-rights,” these neo-Nazis are starting to publicly come out and say ‘look it, hey, I’m brave I’m proud of this’ and we’re sitting here doing this anonymously because we’re scared of them.”
Broadway’s altercation resembles a similar era in North Dakota’s history; a time of national tumult, fear mongering, intensifying racism, purity laws, and the threats of wars. Deep in Fargo Public Library’s microfilm vaults, still available after nearly a hundred years, newspaper stories at the time reflect a mirror image of the 21st century’s second decade.
The Roaring 20s were an age of plenty for the growing middle class, and of sorrow for many agrarian workers. Newspaper advertisements displayed diamond rings for $12.50, society shirts – mostly with collars attached – for $1.29. Ostrich plumes were back in style. Dances at Island Park featuring Harry Smith and his Red Jackets were the bee’s knees on weekends for drugstore cowboys. A brand new Hudson Coach automobile went for $1,250 on the open market.
 Skip past the advertising sections and the headlines are striking. Stories frequently feature the “Chinese problem,” as the Chinese people were banned from immigrating to the United States by the Chinese Exclusion Act. “Aliens blamed for liquor violations,” was another common headline. In January 1923 one story took the front page of the Fargo Forum announcing “Blacks Run Out of Indiana Town” after an anonymous attack on an 11-year-old white girl.
Skip past the advertising sections and the headlines are striking. Stories frequently feature the “Chinese problem,” as the Chinese people were banned from immigrating to the United States by the Chinese Exclusion Act. “Aliens blamed for liquor violations,” was another common headline. In January 1923 one story took the front page of the Fargo Forum announcing “Blacks Run Out of Indiana Town” after an anonymous attack on an 11-year-old white girl.
North Dakota wheat prices were slashed in half. Farmers placed blame with outsiders claiming carpetbagger-types rigged elections from Minnesota hotel rooms. Conspiracy theories alleging grain operators shorted scales, inspectors rigging the system with unfair regulations, became truth.
Political parties polarized. Corruption ran rampant. Farmers began losing lands and profits.
Rising urbanization, the influx of immigrants, stirred angst in Fargo and elsewhere, prompted fraternal organizations like the Elks Lodge, the Oddfellows, and the Sons of Norway for like-minded people to oppose big business.
Isolated. Desperate. Fearful. Deemed an ugly stepchild by Washington D.C.’s politicians, North Dakotans split into two powerful camps: the left’s Nonpartisan League (NPL) and the right’s Independent Voters Association (IVA). The differences between the two parties increasingly left a widening gap, into which walked the Ku Klux Klan.
On January 26, 1923, one of the first headlines referring to the Klan was splayed above the Fargo Forum’s masthead: “K.K.K. Operating in Cass County, Say Witnesses in Fargo Courtroom.”
“America First” became their rally cry, and within two years the Klan was buying ads in the paper.
 “The Klan capitalized on isolationist trends, times of increasing hostility to foreign institutions and influences,” Trevor M. Magel wrote in his 2011 “The Ku Klux Klan in North Dakota” dissertation for the University of Nebraska – Lincoln. The Klan brought nationalism, Prohibition and purity laws, the “Red Scare” portraying their enemies as communists, anti-Catholicism; they also supported high tariffs and legislated unceasingly for immigration restriction.
“The Klan capitalized on isolationist trends, times of increasing hostility to foreign institutions and influences,” Trevor M. Magel wrote in his 2011 “The Ku Klux Klan in North Dakota” dissertation for the University of Nebraska – Lincoln. The Klan brought nationalism, Prohibition and purity laws, the “Red Scare” portraying their enemies as communists, anti-Catholicism; they also supported high tariffs and legislated unceasingly for immigration restriction.
“People felt uneasy about the direction the nation was going.”
Some of the Klan’s meetings were known at the time to be the largest in the nation, attracting thousands as they burned crosses and marched in their white robes, without hoods. North Dakota politicians at times fought the Klan, banning masks in 1923. In 1925 Arthur Sorley, accused of being a Klan member, won the race for the 14th governor by a wide margin. Any allegiance the Klan felt toward Sorley soon broke, however, as his stances softened.
The Klan eventually had enough of niceties, and launched what the Forum called a “Reign of Terror,” bringing baseball bats to marches, beating those thought to be socialists, kidnapped a Casselton man. A meat market vendor in Minot received death threats and K.K.K. signs were pasted onto his shop windows.
Although Fargo lacked a charismatic leader for the Klan’s cause, they found a Presbyterian minister in Grand Forks named Rev. F. Halsey Ambrose to preach the Klan’s rhetoric.
On February 27, 1926, the Kass County No. 57 Klavern Finance Committee in Fargo, Chairman Harry J. Divine, initiated a $10,000 fund drive to purchase the Elks Hall as a meeting place. In a letter currently at the North Dakota Historical Society, Divine raised $3,700 in one night, and up to 400 more members pledged an additional $6,000.
“This is a real He Man’s Organization,” Divine stated of the Ku Klux Klan. “Standing for everything that is good, namely our Flag, public schools, Protestant churches, sanctity of the home and respect for law and order.
“The Kass County Klan No. 5 now has a splendid organization, we have made a nice growth, and we are just rounding into a position where from now on, the organization should be of vital interest to each one of us with so many big things confronting the Real Americans of today.”
 By the end of 1927, the Klan in Fargo and most of North Dakota, fizzled into obscurity. Its demise was brought about by its decision to use violence, which came in the forms of kidnapping, sexual assault, corruption, cross burnings in New Rockford and Fargo, and anti-Catholic rhetoric. Its lack of agreement on a political agenda left followers confused. Infighting followed. The Klan threw a final parade during its 1927 Konklave, complete with a cross with red electric lights attached to an airplane, but only about 1,000 people attended.
By the end of 1927, the Klan in Fargo and most of North Dakota, fizzled into obscurity. Its demise was brought about by its decision to use violence, which came in the forms of kidnapping, sexual assault, corruption, cross burnings in New Rockford and Fargo, and anti-Catholic rhetoric. Its lack of agreement on a political agenda left followers confused. Infighting followed. The Klan threw a final parade during its 1927 Konklave, complete with a cross with red electric lights attached to an airplane, but only about 1,000 people attended.
“It tried to be both a secretive and public organization at the same time,” Magel said. “It tried to be both open and exclusive.”
Some of the Klan’s tenants had a lasting impact in North Dakota. Morality campaigns incited fear and normalized hatred of minorities, which continued long after the Klan was gone. Dueling parties, IVA and the NPL, adopted parts of the Klan’s doctrine they agreed with, such as the IVA adopted the Klan’s reverence for free market capitalism, while the NPL adopted the Klan’s rhetoric about social benevolence, according to Magel.
In time, the IVA merged with the North Dakota Republican Party, and the NPL would go on to become the basis for the contemporary North Dakota Democratic Party.

Grainy photograph of Klansmen in North Dakota – provided by Wes Anderson, director at the Barnes County Museum
Today, the “Tumultuous Teens” in the Peace Garden State have undergone similar upheaval. Prices for oil has been slashed in half. City, state, and national politicians are vying for immigration restrictions. Local news stations claim immigrants carry tuberculosis and encourage long-term residents – naturally primarily white – to steer clear. A new scare has swept the nation, although this time not directed at Soviets but at Muslims, and more recently potential nuclear war with China.
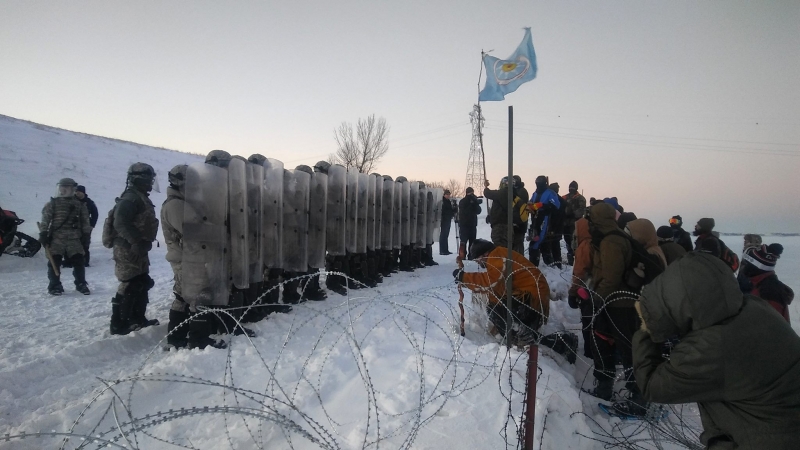
North Dakota legislature proposed new laws in January to target refugees and outsiders – primarily activists involved with the Standing Rock Sioux Tribe against the controversial Dakota Access Pipeline. They’re attempting to ban ski masks, authorize the running over of pedestrians on public highways, and the killing of people running away or resisting arrest for violent crimes. Recently, “purity” legislation laws were introduced to turn Internet routers into “pornographic vending machines,” a service the state would charge $20 per device to use. Legislators also debated the blue laws, some saying Sunday mornings should be spent at home, with a wife serving breakfast in bed.
The 65th Legislative Assembly of North Dakota further proposed House Bill 1427, which effectively states that the Peace Garden State would abide by President Trump’s executive orders and not allow refugees into the state. To disregard the President’s executive order would have an “adverse impact to existing residents of the state,” the house bill stated. Due to hours of testimony against the bill, HB 1427 was slated on February 3 for further research.
After fire debate and hours of testimony last week, the bill was not passed, but an issuance to study the matter further is on the menu. If passed, local governments could impose temporary moratoriums on refugee resettlement and Governor Doug Burgum would have the authority to impose moratorium across the state through executive order. It is a bill that would give communities the ability to evaluate and determine how many refugees it can take in, and stipulates strict requirements for refugee resettlement organizations.
In Grand Forks, Jamie Kelso, director and membership coordinator for the American Freedom Party – formerly known as the American Third Position, a political party initially established by skinheads, is a well-known figure with political ambitions.
Kelso is a bullhorn for white supremacy ideals. He claims he is not a racist, but a “red-blooded American,” and he hosts “The Jamie Kelso Show” for the American Freedom Party. He was once the personal assistant for Ku Klux Klan leader David Duke, and served as a moderator for hate-web guru Don Black’s forum Stormfront, according to the Southern Poverty Law Center, a nonprofit hate crime watchdog.
People today, as in the 1920s, are afraid about the direction the nation is going.
Nationally, President Trump has signed more than 14 executive orders pertaining in part to immigration restrictions, penalizing protesters, halting communication of federal agencies. He has also recruited known fascists into the White House’s inner circles, and is cutting trade relations across the world.
“America first,” Trump said during his inauguration speech. “America first. America first.”

Trump – POTUS Revealed with Kevin R Tengesdal – photograph for a wet plate series by Shane Balkowitsch
Last week, Trump’s nominee for the Supreme Court, Neil Gorsuch, was discovered to have been leader of a student group called the “Fascism Forever Club” in elite high school Georgetown Preparatory, according to the Daily Mail. Trump’s top advisor and chief political strategist, Steve Bannon, is a known white supremacist and former executive chairman of Breitbart News, the main news site for America’s “alt-right” movement.
On February 2, Trump’s Administration reportedly changed the name of the Countering Violent Extremism initiative to Countering Radical Islamic Extremism, effectively reclassifying the initiative’s goals, which according to analysts would remove national attention away from neo-Nazis and white supremacists and focus solely on Islamic terrorism.
“Donald Trump wants to remove us from undue federal scrutiny by removing ‘white supremacists’ from the definition of ‘extremism,’” the largest neo-Nazi website The Daily Stormer reported. “Yes, this is real life. Donald Trump is setting us free.”
Today’s white supremacists are not dressed in sheets, but in suits and ties. They are eyeballing North Dakota’s small and seemingly forgotten towns as big oil funds line political pockets. Known as Pioneer Little Europe, a hit list of eleven towns are being targeted by white supremacists, according to the group’s Facebook page.
Supporters of the Pioneer Little Europe come from all the corners of the white supremacist world, and have been threatening takeovers of small towns since 2015.
The towns of Leith and Antler are permanently marked for takeover under the self-titled Honey Badger Principle. “The Honey Badger Principle states that once an area is marked as PLE-friendly, we will pursue it until we get it no matter what,” page organizers for Pioneer Little Europe North Dakota said on the group’s Facebook page. “In other words: Once we bite, we will never let go.”
President Trump’s use of the phrase drain the swamp, is not a new slogan, Safely said. The phrase was used by Benito Mussolini, Italy’s dictator and leader of the country’s fascist party during World War II. Safely studies World War II history, frequently mentioning similarities between the 1940s and today. He’s never called out a Nazi before, and he took a few days to think about the possible repercussions of his decision.
“‘We all need to be talking about this, and thinking about this, hopefully one day we will say enough is enough and put our foot down,” Safely said. “I would much rather be scared of a Nazi hurting me than being scared of a Nazi controlling me.”









































































































































Leave a Reply