Cyber warfare and misinformation directed at No DAPL activists creates real damage
By C.S. Hagen
OCETI SAKOWIN – An invisible enemy – streaming the airwaves – haunts Standing Rock’s supporters. The nemesis’ presence has long been felt inside the camps opposing the Dakota Access Pipeline, but few had proof of its existence until recently.
Cell phone and live streaming problems were jokes, hidden behind nervous chuckles. Then people began pointing to the ubiquitous airplane circling on the hour, nearly every hour, wondering if their sudden connection issues were created by someone inside. The reports were rumors, conspiracy theories. Soon, few among the thousands could say their devices were not being affected.
The difficulties spring partly from the area’s remoteness and the rugged terrain, but more-so now from what can only be psychological-driven digital attacks. Sudden signal loss, computer files disappearing, fried fiber optic cables, sudden battery deaths from a near full charge, are common. At least one person’s PayPal account was emptied of all monies, according to activists.
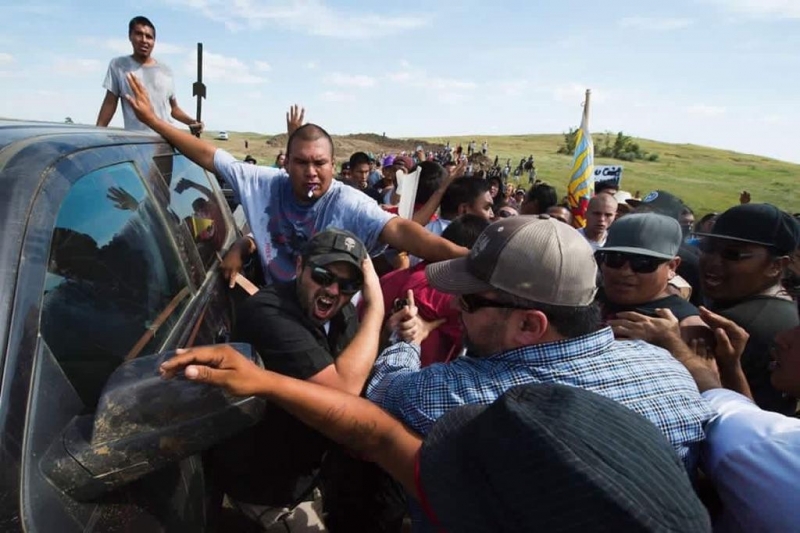
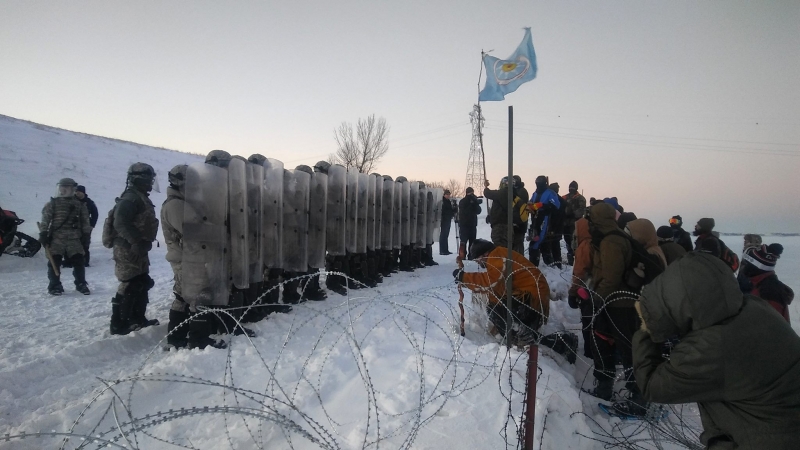
“There is an invisible antagonist winking at us, but no one knows exactly what that means, but we know how it feels,” Ari Herman said. He’s from northern California and is daily at the front lines facing heavily protected law enforcement with tear gas, pepper spray, water cannons, and percussion grenades.
Herman discovered this “antagonist” when he received an email from Google on November 9, reverse traced the email through an IP search and discovered it was sent by a technical department of North Dakota from Fort Totten, approximately 200 miles to the north.
“It’s egregious, and it’s terrifying,” Herman said. “It’s a very sound approach when you think about it. It’s subversion. Less violent. Less costly. I felt it. I felt it was like an emotional waterboarding, it was happening to me and a lot of people. It was creating a very strange aura of suspicion.
“People who announce they are coming to Standing Rock start to have issues even before coming to the state. The precedence this sets is disturbing to say the least.”
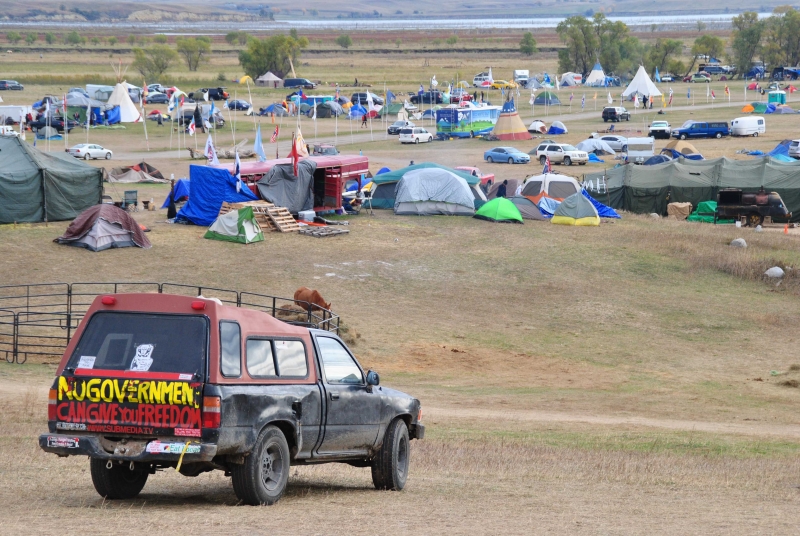
A non-profit organization savvy about online setups in conflict zones, was alerted to Standing Rock’s situation. Geeks Without Bounds, a Washington state organization established in 2010, is an accelerator for humanitarian projects. They’ve been working with the Oceti Sakowin camp since September, setting up Internet and Intranet accesses in specific spots by using a “network hop” to catch the signal from Standing Rock Telecom. A giant geodesic dome, known as the big white dome, donated by participants from Burning Man, became the camp’s first Internet café. Power to run the equipment comes from the sun, and a mini tower called “the stick in the ground on Hop Hill” has been erected to boost signals.
The organization reports many people’s cell phones are acting strangely, and legal observers are documenting and investigating the real threats that come from digital surveillance and communication interference.
Files from long-term criminal defense attorney Bruce Ellison’s computers have disappeared, he said. Ellison is working pro bono as legal team coordinator for the Lawyer’s Guild Mass Defense Committee.
“I know we’ve been investigating a lot of claims of mass data seizure,” Ellison said.
An electronics bug was found inside the Prairie Knights Casino. The device fell from under a table during a meeting inside the Indigenous Environmental Network’s suite, Ellison said. The bug wasn’t sophisticated enough to come from government; he suspects DAPL security teams.
Cyber warfare isn’t the only subversive threat, Ellison said, he knows from experience that agitators and infiltrators posing as activists try to blend in, especially during times of chaos, such as the case of DAPL security employee Kyle Thompson who was apprehended by the Bureau of Indian Affairs on October 27. Police and state’s attorneys called Thompson a victim, and did not file charges against Thompson.
Or the instance when an unknown person came up behind an activist at the front line, pointed at her to police, and then shoved her forward, Ellison said.
“There’s all kinds of stuff going on there that isn’t good, and certainly isn’t democratic. Historically, company security really takes the lead. They provide information to the Federal Bureau of Investigation and other agencies. We suspect that this comes down to corporate security.”
Additionally, video footage shows an FBI agent with the Joint-Terrorism Task Force waiting outside Sophia Wilansky’s hospital door, he said. Wilansky nearly had her arm blown off by a percussion grenade after she was hit, and knocked to the ground by a rubber bullet on November 20, medics and activists said.
“There’s a lot of unknowns going on, and we’re trying to keep our eyes and our ears open.”
After Ellison returned home from Standing Rock approximately three weeks ago, one of his telephone lines connected to the Internet – the only line he used while at the camp – was completely destroyed.
A complete new line had to be installed, Ellison said.
Many at Oceti Sakowin have felt “lost in the wind,” Herman said, without access to their digital worlds. He’s also a writer on The Lego Box Travelogue, and some of his stories have been featured on the Oceti Sakowin webpage. Movements such as Standing Rock’s opposition to the Dakota Access Pipeline need social media and Internet access to grow.
“Living out here under the security apparatus, it’s terrifying,” he said. To a small extent, the experience has taught him as a white person, what it might feel like living as a native person, or black person, or as a LGBT person, he said.
Herman arrived at the camps in early November. “I heard the calling, a little whisper,” he said. “I was ashamed of our treatment of Native Americans, and I wanted to come out here on the ground with my beliefs. This is an important frontier for our relationship with native communities, but setting an important precedent for climate issues… and the climate of surveillance in the occupation camps.” He’s an American, and he’s not against corporations making money, but recognizes the need for change.
“The intimidation is strongly reminiscent of the motto used by the Air Force’s Special Operations Wing in charge of Psy-Ops, “Never Seen, Always Heard,” Herman wrote in his article. He is currently helping out at Oceti Sakowin, he said.
“No one knows for sure who is behind the attacks, but the top suspects include a collusion between Morton County Sheriff’s Department, Energy Transfer Partners’ security and intelligence contractor TigerSwan or another military contractor, the National Guard, and/or the North Dakota Police,” Herman wrote.
Morton County Sheriff Kyle Kirchmeier has repeatedly denied that his agency is involved in cyber warfare against Standing Rock and its supporters. The FBI refuses to answer questions to its involvement in the DAPL controversy, and spokespeople from Energy Transfer Partners and its subsidiary, Dakota Access Pipeline, would not return telephone calls or emails for comment.
Lisha Sterling, the Geeks Without Bounds executive director, said she can’t solve hackers, and she can’t hack back against DAPL or law enforcement as that is illegal and dangerous to Standing Rock.
“What we can do is teach people how to be safer,” Sterling said. “We’ve got encrypted comms options in camp, something called a Mumble server, that anyone can connect to over the Wi-Fi Mesh Intranet if they use that instead of calling each other over the phones their conversations will not be listened in on.”
Encryption is one of the keys to help protect laptops, cell phones, and even personal banking accounts. Also, downloading “Signal” to use for text messaging and for voice calls, turning off automatic updates in Settings, backing up phone data to computer, and being careful to update operating systems, are other ways to help limit hackers’ success rates.
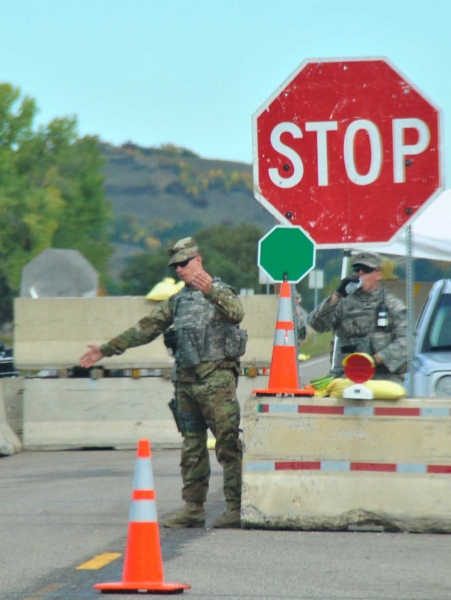
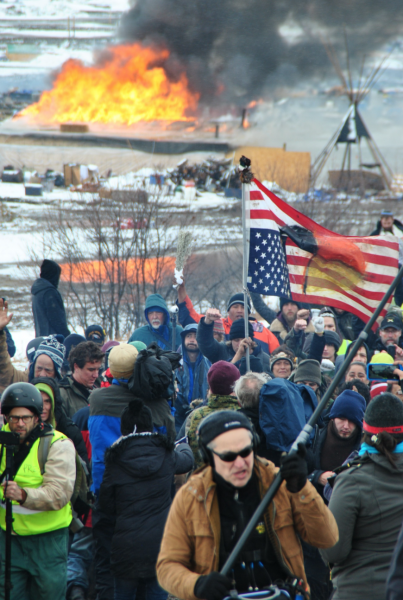
Herman says that another media blackout is currently underway – once again – at the camps, and fears that a police plan is in the works. The FAA has issued another no-fly zone at Standing Rock until December 2, and the “siege” tactics declared by Governor Jack Dalrymple against Standing Rock, authorizing police to fine anyone hauling supplies to Standing Rock up to USD 1,000, and threatening to take away emergency response teams is only part of the state’s strategy.
The legal repercussions are not known, even more ethereal are legal strategies to combat these digital wraiths. “I can tell you I was really pissed off when I found out who did it, I was surprised…” Herman said.
His voice scrambled on the phone, like listening to an AM radio station halfway tuned in. And then the line went dead.
Radio, Facebook, and hacks
Last week, Anonymous, the international network of activists and hacktivists, threatened Morton County Sheriff’s Department, and allegedly destroyed its website and Facebook pages. On Wednesday, a new Morton County Sheriff’s Department Facebook page, followed by more than 600 people, reported the following:
“Greetings, everyone. We’d like to formally apologize for being ignorant f*cks. We know no better. We are privileged and do not understand the importance of water and its connection to the essence of life. We do not believe in science, climate change, or sustainability. Sincerely. The Pipeline Pigs.”
On Tuesday, the Facebook page posted: “On this white and snowy day in North Dakota, we’d like to announce that our pig heads are so bloated, we think we have the authority to illegally interfere with interstate commerce. We think we can trample over the constitution with our cloven hooves. We are looking to hire lawyers as we can face jail time for violating the Constitution and people’s civil rights.”
A different Morton County Sheriff’s Department Facebook page has cultivated approximately 30 followers, and appears to be Pro DAPL, or at least supportive of government decisions to restrict emergency services to Standing Rock, and to fine anyone carrying supplies up to USD 1,000.
“Soon there will be nothing to keep those crybaby anarchists fed and warm but peace signs and prayer,” the alternative Facebook page reports. “It’s been fun terrorizing them, but all good things must come to an end. Us boys in blue are starting to get chilly, even in full combat gear we’re wearing. Time for you hippies to give up and move on. No more supplies, no more emergency services, take the hint already… Love being evil.”
There is also two more Facebook pages, one called Morton County Sheriff Department, which appears to be a venting platform.
Scott Hennen, a partner at Flag Family Media, who broadcasts on stations such as KFYR 55 AM Bismarck and WZFG 1100 AM Fargo, called the activists at Standing Rock “sick,” “a group of lawless thugs,” and “eco-terrorists” on his Facebook page. He believes North Dakota should sue the federal government, according to Facebook posts.
On Monday, Hennen interviewed Morton County Sheriff Kyle Kirchmeier, reporting 110 days had passed since the beginning of the “siege,” as Hennen described the situation outside of Cannonball.
Kirchmeier won’t send law enforcement to clear Oceti Sakowin, and doesn’t expect federal assistance, “as long as the current administration is there,” the sheriff said during the interview.
“I’ve heard stories of rampant drug use and rapes, I don’t know, they’re just stories,” Hennen said. “Do we know what’s happening in the way of lawless behavior in the camp?”
“There is definitely, the alcohol, the drug use, the sexual assault, we do have reports of that.” Kirchmeier said, adding that such reports are forwarded to the Army Corps.
Henner praised Dalrymple’s decision to stop emergency responses to the camps. He called a lawsuit against Kirchmeier and the Morton County Sheriff’s Department’s use of excessive force “bunk.”
“Law officers have been shot at, spit on, had feces thrown at them, had their families terrorized – and now they’re being sued. Throw it out of court – along with the violent extremists invading Morton County.”
Hennen’s claims have been called lies by people supporting Standing Rock.
Dalrymple’s orders
On Wednesday, the governor backtracked the seriousness of his emergency evacuation message, saying that law enforcement will not be hunting Standing Rock suppliers, or arbitrarily stopping people. He also petitioned for a meeting with Standing Rock leaders, he said, and wants to discuss how to rebuild the relationship between the tribe and the state.
“We want the entire public to know that this is not a safe place,” Dalrymple said. During a press conference reporters asked Dalrymple why call the emergency evacuation if he wasn’t planning on cleaning the camps out.
“We get that question every time there is a flood too, what purpose does it serve. It is an official notice from the state, from the National Guard, from law enforcement that we may not be able to help you in an emergency situation. No, we are not going to be having roadblocks or stopping vehicles.”
Dalrymple’s assurances did not ease activists’ fears near Standing Rock late Wednesday afternoon, especially after an online report that a Red Cross shipment was stopped by North Dakota National Guard.
Lynn Speral, chief executive officer for American Red Cross Dakotas Region, said she was aware of the online reports, but that the American Red Cross is a neutral organization and is not assisting anyone involved in the DAPL controversy at this time.
“If things would warrant a disaster type relief response, such as cars stranded because of a storm,” then her organization would respond. “But the situation there is not one that requires the American Red Cross’ assistance, Speral said. If Standing Rock required blood then the supplies would not come from the American Red Cross.
Dalrymple also said he has never contemplated using National Guard or federal or state officers to forcibly remove activists from Army Corps lands. The pipeline is finished everywhere in North Dakota, 95 percent complete, with one exception: under the Missouri River at Lake Oahe.
“To change the route now is probably not feasible,” Dalrymple said.
Lieutenant Governor Drew Wrigley said the state will not be held responsible if serious injury or death occurs at Oceti Sakowin. “They’re there without a permit… they’ve stayed through many seasons. This snowstorm was predicted several days in advance, all of it was out in the media. At some point there’s an assumption of risk, there’s a lot that’s involved and I don’t mean to make light of any of it. There are some people there who probably don’t know anything about this weather.”
Emergency response crews will attempt to respond to calls, Dalrymple said, but arrivals will not be guaranteed.
Dalrymple further mentioned that he has had no official offers from Kelcy Warren, CEO of Energy Transfer Partners, to pay government costs, which are expected to reach a total USD 17 million.
“I don’t even know if it’s possible,” Dalrymple said.
A decision for Morton County to accept any official offer would not rest in the governor’s lap, he said.
Dalrymple also stated during a press conference that his office has been in constant contact with Standing Rock Sioux Tribe Chairman Dave Archambault II, however; according to an official request for information filed with the governor’s office approximately six weeks ago, the governor had no contact with Archambault’s office during a two-week period when tensions were heightening between the state and the tribe.
Ladonna Tamakawastewin Allard, a historian and owner of the Sacred Stone Camp lands, said the governor’s office doesn’t understand the tenacity of the Standing Rock Sioux tribe and its supporters.
“We have been here for thousands of years,” Allard said. “We understand North Dakota winter. When they first issued the order to cow the Indian people, to get back to the reservation, there was a blizzard. And the winter was hard. And the Indian said, ‘Who moves in a blizzard?’ Now we come to 2016 we’re saying the same thing, ‘Who moves in a blizzard?’
“We are not going to back down. We are not in anyone’s home, we are in our own home. Awake. We are in our own home, from the Heart River, to the Platte River, to the plateaus, to the Missouri, 1851 is the supreme law of the land.”
She believes in the rule of law, but says that it is no longer working.
“What do you do against injustice? You stand up, you stand in prayer, you stand in the best way you can. So the governor doesn’t understand prayer. The governor doesn’t understand that the real power is the people, and the real power has always been the people, not a corporation. I think we are seeing that today, where the people are saying ‘We need to change.’ We are not standing down. We are in our home. We are strong, and we have prayer. The governor has no idea what he’s facing.”