101 years after the Armenian Genocide began, the world still refuses to recognize the atrocities
By C.S. Hagen
BAKU, SOVIET UNION – An angry humming noise kept Karine Eloyse Pirumova from her windows. Curtains drawn, she knew the cacophony was heading her way. Despite the fact her husband had begun sleeping with a knife under his pillow, she refused to believe the rumors, until her telephone rang one afternoon mid January 1990.
“We need to flee the city.” Karine’s twin sister’s voice was panicky. “I’ve just been let go. It’s not safe for Armenians in Baku any longer.” They hurriedly agreed to meet at Karine’s apartment.
The line fell silent. Her sister, Marine, was let go? She had a good job working as a communications specialist with the Caspian Shipping Company. She glanced around her government-supplied apartment. Where to go? What to take?

Pirumova sisters looking over a recently-published Russian book about their family history – photo by C.S. Hagen
Andrey and Genna, her young sons, played contentedly with their toys. Supper simmered on the stove. Pictures of the Pirumova family, once Armenian generals and nobles, hung from her walls. Karine had heard the news of lootings and beatings, not through heavily censored Soviet news broadcasts, but through her Russian husband, who spoke the local Azerbaijani language. She never dreamed the violence could reach their doorstep.
Hands trembling, Karine packed a small suitcase. Her father’s nearly forgotten stories sent chills down her spine. As a child, her father, Abesalom Pirumov, had seen his mother gunned down in the streets. Her dying words to him were, “Run, my children,” Karine said.
“It was the first thing I thought of. And after 70 years it was happening to our family again.”
“Life was getting hard in 1988,” Marine, Karine’s sister, said. Her hometown, a seaside port in the Soviet Republic of Azerbaijan, was relatively peaceful until the unrest began. Muslims and Christians lived as neighbors with few incidents. “But we kept living our lives. Baku was an international city. We could not believe that in modern Baku this kind of thing could happen again. Just like in 1915. Killing people. Robbing. Raping. It was the same story.”
Karine could almost decipher a chant coming from the rioters in the streets below her apartment. What was to become known in history as “Black January,” Baku city’s Muslim-led pogrom to eradicate Armenians due to ethnic tensions over land claims, had begun.
No time to pack pictures or jewelry. Food was important. They would need water, and money. In those days, and in the Soviet Union, no one had bank accounts. Cash was the only recognized tender, something of which she had precious little.
Karine stiffened. The chant became clear. “Out! Armenian Christians. Out!” Karine, pronounced Ka-ree-na, told her boys to start calling her Katia, a Russian name, instead of her given and easily recognizable Armenian one.
Marine traveled fast as she could to her sister’s apartment complex. The roads teemed with people. She kept her face lowered to hide her white complexion. She said there was no time for her to return to her apartment to pack a suitcase.
“I heard screaming,” Marine said. “It was a woman’s voice. And this time I was scared. I asked myself why hadn’t I left already?”
X Marks an Armenian
The systematic destruction of anything Armenian left approximately 300 dead, and forced 250,000 Armenians into exile in January 1990, according to a 2010 conference made public by the Armenian National Academy of Sciences. From the South Fargo home of Jim and Eloyce Kenward, Karine’s sponsors, the sisters spoke of a secret list marked with X’s for every Armenian in Baku.
News was heavily censored. Information was blocked. The pogrom was a direct response from Soviet Azerbaijan to the Armenian demonstrators urging the Kremlin to allow Karabakh back into Armenia. Both Armenian and Azerbaijani held claims to the area, which had long before belonged to Christian Armenians.
“In 1923, Stalin gave this land to Azerbaijan, and under Gorbachev, Armenians decided to take this land back,” Marine said.
The protests sparked Azerbaijani hatred, long simmered to coals during Soviet occupation. In an attempt to quash the Armenian movement, special forces called Azeri Omon initiated the pogrom in Sumgait in 1988, and later in similar assaults in Kirovabad, Baku, and in Karabakh, according to the Armenian National Academy of Sciences.
Exact numbers of Armenians killed in 1990 are still a mystery. In 2010, the director of the Center for Caucasus Studies at Moscow State Institute of International Relations, Vladimir Zakharov, said xenophobia was always a problem, even under Soviet rule.
“Hatred against Armenians passed on from generation to generation and today the image of Armenians as an enemy to Azerbaijan is propagated at the national level,” Zakharov said.
Hatred, Karine said, that her father knew well. Despite the fact that he watched his mother gunned down, that the family mansion and surrounding city was burned to the ground in 1920, and that he was forced to flee to Baku, her father did not reciprocate the hatred.
Once nobility, and at the tender age of 13, he fled the family’s grand ancestral home in Shusha, Nagorno-Karabakh, with nothing but the clothes on his back. He survived, and later married a tailor’s daughter, Evgenia Pirumova, and raised twin daughters and one son. He rarely spoke of the troubles of 1920, except to weep openly when he spoke of his mother. He never uttered a harsh word against the Soviet Union, even after his brother was imprisoned for 17 years under Stalin’s regime for crimes against the communist state. Like the Pirumova sisters, his family in 1920 never expected the violence to reach such a crescendo. A recent book published in Russian entitled Pirumov and Pirumova by Yuri Pirumov, shows pictures of extended family, once generals, intellectuals, and revolutionaries, and the family mansion, now in ruins.
Destitute and orphaned, Abesalom survived the 170-mile journey from Shusha to Baku. Other family members, including the Pirumova’s maternal grandfather, was forced into the death caravans and into the Syrian Desert. He too survived, but rarely spoke of the ordeal while Karine and Marine were young.
A bookkeeper by trade, Abesalom’s aspirations in life were to sleep peacefully at night, and never overstep his bounds. He was an honest, hardworking man, who sipped a little vodka to calm his nerves at night.
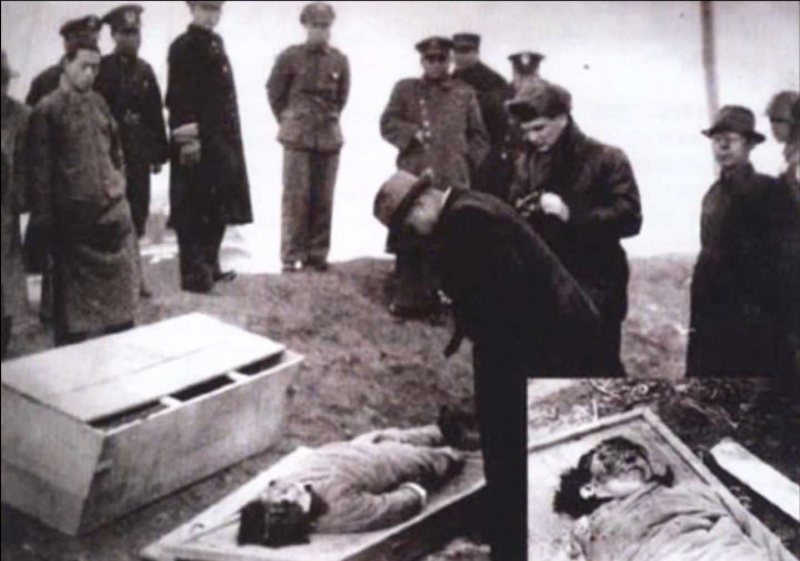
During the first pogrom against Armenians by the dying Ottoman Empire, which began on April 24, 1915, more than 1.5 million Armenians were massacred in what most historians now call the Armenian Genocide, according to the New York Times and the Armenian Genocide Museum. Some scholars claim the “Great Crime” was the first genocide of the 20th Century, even though the word genocide was not coined until after World War II.
During the first phase of the organized extermination, young men were conscripted into the Ottoman army, then forced to give up their weapons, dig their own graves, and face firing squads, according to the Armenian Genocide Museum. The second phase began with the arrest of several hundred Armenian intellectuals and elite, who were summarily beheaded. Mass exile began the third phase. Thousands died from organized attacks along the way, epidemic disease, and starvation, according to the Armenian Genocide Museum. The forced marches, nicknamed “Caravans of Despair” sent thousands of Armenians into the Syrian Desert, only to be attacked by Sultan-backed bandits, according to the Armenian National Institute.
American Ambassador to the Ottoman Empire before and during World War I, Henry Morgenthau, reported on the widespread slaughter vigilantly, and later wrote a book called Ambassador Morgenthau’s Story.
“Cold-blooded, calculated state policy,” Morgenthau wrote. “I am confident the whole history of the human race contains no such horrible episode as this.”
Escape to Moscow
Under cover of night, the Pirumov family piled into a Lada taxi. The driver was a friend. Streets teemed with rioters. Men with clubs banged on the taxi’s hood, peering inside, asking if Armenians were inside.
The twin sisters crouched low, covering their dark hair and faces as best they could. Andrey and Genna clung to their mother’s waist.
“No.” The taxi driver waved the rioters away. “There are no Armenians in here.”
The drive to a Russian friend’s home was tense, Karine said. “I don’t know if she hadn’t heard the news, or if she was a hero, but she rescued us.”
Despite the growing violence, family friend Marina Korchazhkina endangered herself by giving food and shelter to the Pirumov family for two days, Karine said, until she received word a ship from her trading company could ferry them across the Caspian Sea to Krasnovodsk. During the wait, the sisters learned both their houses had been burgled.
“The very next day men in leather jackets robbed my house,” Marine said. She was single when the troubles began. “If I had been there, I would have been killed.”
While in hiding, the sisters’ also discovered their cousin, Melik, was attacked and nearly beaten to death inside a public bus. If the driver had not taken pity, he might have died, Karine said.
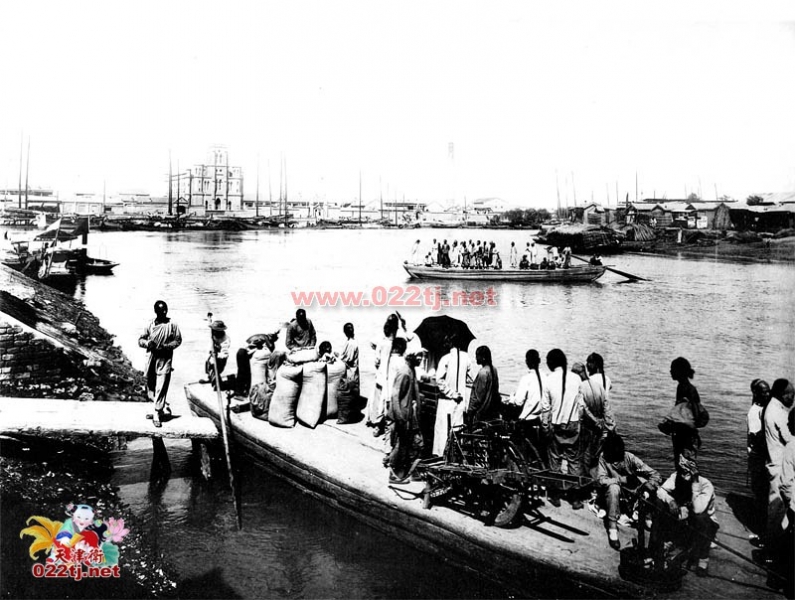
At the shipyard along the Caspian Sea, however, the Pirumovs and thousands of Armenians found some semblance of safety. The growing crowd pushed and shoved. The winter cold was bitter during the hours long wait. Azerbaijani ship crew teased the crowd, lowering the narrow gangplank to arms reach before hoisting it back up, Marine said.
“And we still weren’t sure if we would have been thrown off the ship,” Karine said. But the Pirumovs had no other place to go.
Soviet troops made their presence known throughout Baku, Marine said. “But it seemed they were waiting around for orders. Eventually, some soldiers started to help, like when we were at the shipyard they surrounded us. They were controlling so it was good.” Their encirclement kept rioters at bay, Marine said.
At midnight, the gangplank hit the dock. The crowd jostled forward. Marine screamed at the crowd to board slowly, for the walkway was narrow, and the icy seawaters below would surely swallow anyone who fell. Once on board, Marine found the captain, a former co-worker, who gave them a cabin.
“There were hundreds of people sleeping in the hallways,” Marine said. “We were very fortunate.”
From Krasnovodsk the Pirumov family traveled by plane to Moscow, at one time sneaking Karine’s two sons on board while Marine asked the captain for assistance, which was given. “The Russians were sympathetic,” Marine said. “But the Soviet government did very little to help, many times troops who were supposed to be protecting us turned their backs on us or stood there and watched.”
In Moscow, they stayed with their brother until kindly villagers accepted them in. Karine remembers being treated as an outsider because of her black hair. When her family was given an apartment with two rooms, neighbors bickered. She responded by telling them hard work, and no vodka, was her secret.
Refuge in Fargo
Marine was the first to see the Statue of Liberty from an airplane. Months of waiting in lines, bribing Soviet clerks, procuring the proper documents as a refugee took its toll, but when she landed with twenty dollars in her pocket, she felt happiness, and peace.
Her sponsor, Lutheran Social Services, had arranged for her to travel to Fargo, North Dakota. She had never heard of the city or the state before, saw on a map it was close to Canada and wondered if Fargo was cold.
“But I was so happy I was going to the United States, I didn’t care where I was going.” Marine laughed. “I wondered if I could go to South Dakota because it sounded warmer.”
Lutheran Social Services offered Marine a job as a butcher, but she refused, saying she needed to learn English. Her first job was at Kmart, and although she wanted to work in the back, away from people, Kmart managers placed her at a cash register.
“I was afraid I wouldn’t understand,” Marine said. Both sisters no longer have English problems. Their Slavic accents are a delight to the ear. “And I learned quickly when I was on my break to take off my work vest, or customers would ask me questions I could not answer.”
She met the Kenward family through Olivet Lutheran Church, who agreed to become her sister’s sponsor.
“We met 24 years ago,” Jim Kenward said. “And since then we haven’t broken ties. Their family is our family.”
“I am so thankful to them and to the United States,” Marine said. “Our father lost everything, and we lost everything.”
Karine and her two sons arrived in Fargo years later and because they no longer held the status of refugees they arrived as “Privileged Immigration Parolees,” Karine said. She held up the documents proudly to prove it.
In Fargo today, the Pirumovs can find some of the comforts from their former lives. Karine cooks traditional dishes at home. Marine and her husband opened their own business, Anytime Transportation, and employed Karine as their bookkeeper.
“I am so glad I came here,” Karine said. One of her sons graduated from North Dakota State University, the other from Concordia College. She found Marina Korchazhkina, their savior in Baku, on Facebook, and is in frequent contact.
When asked about President Obama’s recent failure to publically recognize the Armenian troubles of 1915 as genocide, Karine sighed. “If genocide had been recognized by the world when this happened, maybe today would be better. Maybe, it wouldn’t have happened to the Jews.”
With the recent rise of ISIS near their home country, the Pirumova sisters are disturbed. There is little difference with the terrorist group’s systematic slaughter to the Ottoman savagery, or the 1990 Azerbaijani pogroms, they said. Armenia, ancient land of the Hittites, once the most powerful kingdom east of the Roman Empire, now a fledgling republic established in 1991, is the only Christian bastion in Central Asia.
“I am always thinking about the refugees, because I was one of them,” Marine said. “America takes immigrants, and this is what I appreciate about the United States. We are a country of immigrants.”

Safe in Fargo, North Dakota, the Pirumova sisters enjoying cake with the Kenwards – photo by C.S. Hagen