A Yazidi family’s journey from war-torn Iraq to America
By C.S. Hagen
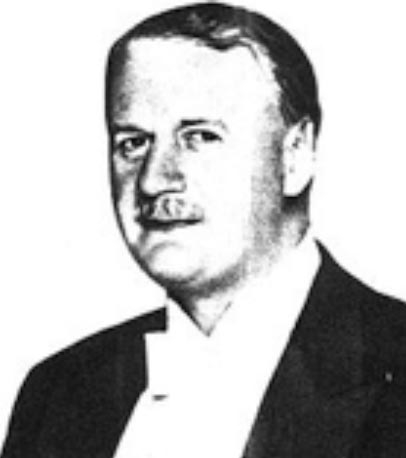
MOORHEAD – Today, Ezzat Khudhur Alhaidar is safe from ISIS guns, but the memories of war still haunt him. In 2005, he donned a U.S. Army uniform and began working as a front-line interpreter, a position that put food in his belly and a target on his back.
He leans back into a leather sofa while his wife, Zaman Alo, finishes setting a makeshift table with a mound of biryani, steaming hot chickpea soup. Onions covered with sumac follow. Four more dishes take up the table’s last inches, which doubles as a nightstand: homemade pickled green tomatoes, olives, a sumac salad, and chicken kabob pieces, tastes of Alhaidar’s homeland in Iraq. He bemoans the lack of proper Iraqi kabobs, also known as kafta; the taste here is just not the same.
Volume blaring, Alhaidar’s five children finish watching “The Emoji Movie.” After only three years in America, his eldest children speak English with ease, explaining the movie’s plot. His second youngest daughter performs cartwheels with the grace of an Olympic athlete on the living room floor. The apartment walls are sparse; few pictures or decorations accompanied the family on their flight from Iraq, but the apartment is home and it’s safe.
They’re Yazidi, an ethno-religious minority, persecuted for centuries because of their adherence to Yazidism, the oldest Mesopotamian religion. Alhaidar obtained U.S. visas three months before the most recent pogrom against Yazidis began, watching news reports helplessly of neighbors and family fleeing before ISIS’s onslaught.
When Saddam Hussein was captured in 2003 during Operation Red Dawn, Alhaidar remembers feeling relief. During Hussein’s reign, no one dared breathe the dictator’s name, let alone speak ill of the government. If suspected of dissatisfaction, one could face flesh-eating acid in one of multiple torture chambers, Alhaidar said. Few came out alive.
As a child when he saw police, he remembers shivering with fear. “It was not life,” Alhaidar said. “We were the happiest people when we got rid of Saddam, but we didn’t know after Saddam, a thousand Saddams would come to the country. If there was a choice between now and Saddam, we would not choose Saddam.”
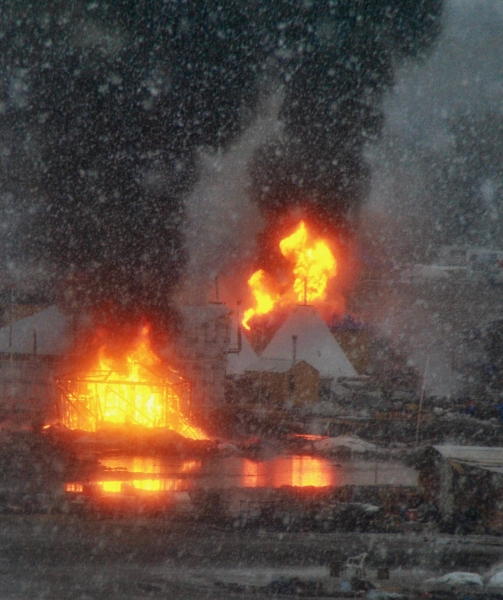
The ISIS invasion of Yazidi areas came quickly in 2014, with no time to raise alarms. The Peshmerga, the Iraqi Kurdistan forces, promised safety but fled before oncoming ISIS troops. One night, Yazidi villages went to sleep and awoke the next morning with ISIS in charge.
And then from 6,000 miles away, Alhaidar watched as the slaughter began.
The Yazidi people are regarded as people of a different faith who need to be killed or converted to Islam. Once before, they were targeted by Muslim extremists, primarily Sunni jihadists, after the US invasion of Iraq in 2014.
ISIS jihadists have been mostly beaten back, but Alhaidar’s relatives still have no home. After the massacres began, Alhaidar managed visas for his mother, a few nephews and nieces, from America, but other family still remain behind. They live in refugee camps and are unable to return home.
More than 40,000 Yazidis fled to Mount Sinjar, identified as the final resting place of Noah’s ark, and nearly half a million people poured into Dohuk, the Kurdish north, in one of the largest and most rapid refugee movements in decades.
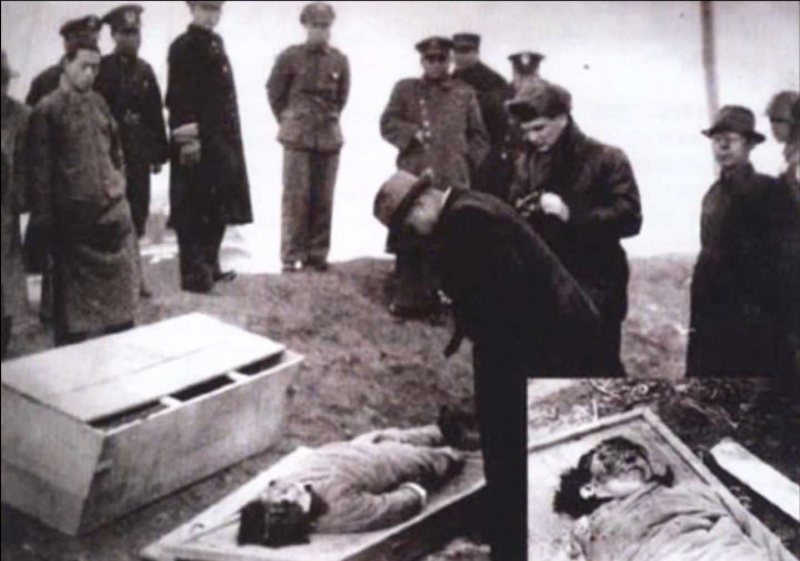
Villages were decimated. More than 5,000 people were killed in two days. Another 7,600 women were kidnapped and forced into sexual slavery, many still missing. No less than 3,000 children were sent to brainwashing, indoctrination schools to learn how to become future terrorists, Alhaidar said.
Most of the ISIS forces were recognizable faces, Alhaidar said, coming from neighboring towns, and not foreign fighters.
“What can we expect of these kids in the future?” Alhaidar said. “We were crying over here. ISIS attacked my people. People have become hopeless, homeless.”
Growing up hard
At 16, Alhaidar rose with the sun to haul bricks on his back. Not manageable red baked bricks but heavy construction bricks, with a daily quota of 100, for $25 in pay.
“Life is hard, sometimes, and harsh, it can crush you,” Alhaidar said. “But I got a lesson from the bricks: if I didn’t go to school I knew I would spend my life hauling those bricks.”
In ancient times, Yazidi culture and religious rituals were passed orally from generation to generation. They do not have their own schools, and mosques were avoided to deter conversion.
Historically, the Yazidi have been attacked repeatedly by neighbors. Atrocities were recorded by researchers, historians, and writers, such as Henry Austen Layard. One genocide occurred in Shekhan Province, close to Mosul, after fleeing Yazidi were trapped along the Tigris River due to spring flooding. Yazidi women jumped into the river to escape conversion, according to Laynard.
A second genocide occurred in Sinjar Province, when Ottoman soldiers beheaded Yazidis.
The Alhaidar family is originally from Sinjar, but his parents fled from oppression to a village called Kabartu, where Alhaidar was born. Later, Hussein’s regime destroyed their village and grouped 12 villages into a collective called Omayya. After Saddam fell from power, the collective was renamed Khanke.
Although the villagers were also Yazidi, Alhaidar’s family was never accepted into the community, he said. Alhaidar’s father, formerly a shepherd, became a day laborer to put food on the table, and life for his family was difficult.
“They were always higher, as we were not from that village,” Alhaidar said.
Life became harder after his father died in 2004. Without money to take him to the hospital, his father asked a friend for help, but he passed away the next day.
“After my father’s death, my life became harder, and I felt that I had to walk alone with no support,” Alhaidar said. “My brothers and sister and my mother were in the situation, and were doing their best, yet nothing could be compared to my father. Before my father’s death, we would barely think about the tough or hard side of life.”
In 2013, the government handed out land parcels to the villagers, but not to his family. “They were mean, and they were always the people of the situation, nobody could raise their face to say ‘Hey, we’re over here.’”
“We were always getting attacked by those around us, and by that I mean Muslims,” Alhaidar said. “The only reason we were oppressed was because of our religion, which makes it difficult to maintain our culture.”
He began studying late into every night at the Iraq University of Dohuk. College was free, but he still needed money for food, clothes, and lodging. Some days, he borrowed clothes to attend classes. A brother helped with a loan of 500 dinars, the equivalent of $300.
While his friends were getting married and buying cars, Alhaidar worried about enough cash for his next meal. A dowry for marriage seemed an impossible dream. He spoke his native Kurdish, also Arabic and English, and saw opportunity when U.S. armed forces came, once again, to his homeland in 2003.
He signed up as an interpreter.
“That decision changed my life,” Alhaidar said. “And it changed the lives of all the people around me. Because of that decision to join the U.S. Army, I brought 28 people to the US and they are working, smiling, while if they were left over there, whatever you say is not enough, at the very least they would have no jobs.”
As a U.S. Army interpreter
“If you were a minority, you were gone. If you were US Army and coming from vacation, you were gone,” Alhaidar said about a lonely road he frequently had to travel. “Gone” means a quick bullet or indefinite imprisonment for exchange. Al-Qaeda terrorists would not frequently target military Humvees, but rather the vehicles following behind.
“I was an easy target for them,” Alhaidar said.
Being Yazidi and an interpreter for an invading force, and frequently meeting face to face with terrorists during interrogation sessions, meant he had to take extra precautions. Frequently, suspected terrorists were interviewed, then released two weeks later.
“We were safe, but we were scared to go anywhere,” Alhaidar said. He always watched for tailing cars, never went to Mosul. Terrorists targeted interpreters and their families. Stories of fellow interpreters ambushed by terrorists kept him on edge. Such as the story of one man who broke 27 bones during an Al-Qaeda sneak attack.
Before joining the US Army, food was scarce. Afterward, he could eat his fill. “You could smell the food a mile from the restaurant,” Alhaidar said.
He went on duty for 45 days in a row, then came home for six. He also worked as an advisor for US troops, helping differentiate between friend and suicide bomber. When he saw indiscriminate shooting, it was one of his jobs to stop the soldiers or private mercenaries and tell them the differences between Orange Zones and Red Zones, the latter meaning dangerous areas.
The stress of war, constant vigilance, leaving his home country to start a new life in a strange land, has taken its toll, Alhaidar said. He opens a kitchen cupboard and returns with a brown paper bag, filled with prescription medicine for PTSD. He’s improved over the years he’s lived in Moorhead, but is filled with a longing to help his people, as well as the new American community in Fargo/Moorhead.
He’s tried for help at the local Veterans Hospital, but was denied. The U.S. Army does not consider him a veteran.
“We wore the same uniform, wore the same boots, went on the same missions, and could be killed at any moment in Iraq and Afghanistan, but unfortunately, today, they do not recognize us as veterans,” Alhaidar said.
“It’s not about money. The U.S. Army was a school, and I was proud to be a student in that school. I was a part of it. But they said ‘No, rules are rules.’ Even if they could consider us veterans, and not pay us anything, that would be fine.
“Are you a veteran?” Alhaidar pretended to be military doctor questioning himself.
“No. I don’t have a paper. So what do they call it when I was working with them? Part of our duties meant that if we weren’t there, many more US soldiers would have been killed.”
Additional duties included interpreting any communication between Iraqi and US forces, talking with village leaders, learning where the dangerous spots were, and locating IEDs.
Alhaidar was injured once when his Humvee was ordered to lead a nocturnal drive without headlights and they smashed into a gravel pile. He marched with soldiers into war, accompanied searches for terrorists going house to house, relayed information quickly under fire.
“We were between them,” Alhaidar said. “We would know who was lying and who was a danger.”
Once, a commanding officer known to Alhaidar as Captain Kingman, ordered him from the safety of a Humvee to accompany an ambulance into Mosul Province.
“Even a crazy person wouldn’t go into Mosul in an ambulance,” Alhaidar said. “No armor, no protection.”
He survived, but the same captain also required him to translate while he cursed elderly village leaders. “And you know, in Iraqi community, that was not allowed,” Alhaidar said. “We were there to protect people.”
The U.S. Army had one rule he can’t forget: never chase terrorists if they ran away.
“These bitter moments gave me lessons in life,” Alhaidar said. “I’m a new American, but even in Iraq I was American in my soul.”
Because of his role helping the U.S. Army, officials said he would be protected, but Alhaidar waited more than a year before obtaining a visa, during which time he saved enough money to purchase a house and find a wife, with a $7,000 dowry.
After he left the military in 2012, he worked as a teacher with Weatherford, an oil company. Working 15 days on and 15 off, he also started a computer shop and a learning center for teaching English as a second language.
America
Over sips of cloying Iraqi tea, Alhaidar knows he is one of the more fortunate interpreters, one of thousands who worked with the U.S. Army during its post-9/11 military operations. In exchange for their services, Iraqis who collaborated were promised special visas, but the Special Immigrant Visa program became backlogged. Some are considered traitors by insurgents, and are actively hunted. Identities were kept secret.
President Donald Trump’s Administration travel ban has recently created new obstacles for the Army’s former Iraqi partners, and many are being denied visas.
In May 2014, however, Alhaidar packed his family’s lives into eight suitcases. He filled four with his most precious possessions – books – some Kurdish, some Arabic, and others in English. Hard drives and photo albums, the only transportable keepsakes he could bring, went into another suitcase.
Traveling through Jordan, his family landed in Chicago after a 14-hour flight.
“Everything was green, everything was beautiful, but we still knew our trip was not done,” Alhaidar said. A type of sadness came over his family during their layover in Jordan. Their home for countless generations seemed far away.
Today, Alhaidar has three bachelor’s degrees, and is active in community development. Neither Republican nor Democrat, he believes in dealing with issues, and not following a political line. He’s building a nonprofit organization, and is active with Mindful Seeds, a leadership program in the Fargo/Moorhead area.
Settling into America hasn’t been easy, but slowly, his children are growing used to the area. Alhaidar’s wife is in school, and he has found work, but is looking for more meaningful employment, perhaps one day in politics.
“Life has started to smile on us.”
With recent hate crime incidents in Fargo, seven cases so far in 2017, Alhaidar challenges people to make attempts to understand world events. He is no stranger to hate crimes. In Iraq, he was part of a close circle of friends including engineers, doctors, veterinarians, and technicians, with himself as a teacher, who once, when life was simpler, enjoyed picnics, a few beers, and music together.
“Due to tensions, discrimination, sectarian religious and political issues, and adding to that, ISIS attacks, there is barely anyone left in this group anymore. They all left the country. Each went to a different country, whether in Europe, America, or Australia, to start a new life away from their childhood memories.
“Life is about stepping toward each other and building trust,” Alhaidar said. “Even white supremacists we should listen to. We have to be careful of our daily actions, and see Fargo/Moorhead as a colorful community. Today, the life of Moorhead is the life of our kids.”