State worked with TigerSwan to ensure “battle rhythm,” second DAPL security worker whistleblower steps forward
By C.S. Hagen
CANNON BALL – The lawsuit against TigerSwan for illegally working security in North Dakota is a civil case, but proof now exists that cyber warfare tactics were used against activists at the Standing Rock camps, according to IT analysts. One question remains: who was responsible for launching the attacks?
Hundreds of mobile phones and vehicles were damaged as batteries were suddenly drained of power, or were “fried,” during warm and cold weather. Incidents of random hot spots for Internet reception with alternating GPS locations, hacked laptops and cellphones, are too many to count. Bugs or listening devices were planted in meeting rooms at the nearby Prairie Knights Casino & Resort. Fiber cable boxes were broken into. Additionally, cars en route to and from Oceti Sakowin broke down without warning, and have not been the same since.
Morton County Sheriff’s Department denied that their deputies used cyber weaponry, but leased a mobile cellular tower from Verizon to boost reception. The Office of the Governor of the State of North Dakota claims it was unaware that TigerSwan was operating illegally, and yet was in the loop, keeping the “battle rhythm” alive. The National Guard is considered a “law enforcement multiplier” under emergency situations, and police are not in the business of digital disruption, preferring to operate in the legal gray zone of electronic intelligence gathering. Possible suspects that remain include the federal government and TigerSwan, the North Carolina security firm whose services were paid by Energy Transfer Partners, the parent company of Dakota Access LLC.
Headed by former Delta Force officer James Reese, both Reese and TigerSwan face a civil lawsuit filed by the North Dakota Private Investigation and Security Board for illegally working in the state despite repeated warnings.
The cyber and cellular attacks at Standing Rock on activists ranged from malware, IMSI catchers, to electromagnetic field devices, IT analysts report. Malware typically comes as viruses through emails, links, or attachments and acts with stealth, not programed to alert the owner. IMSI Catchers – sometimes known by the brand Stingrays – act as fake cellular towers, forcing GSM phones to connect and then suck in data. The electromagnetic field device is a cyber weapon used in the Middle East to block cellular phones sending data to Improvised Explosive Devices, or IEDs. It is a short burst of electromagnetic energy meant to disrupt or damage nearly any equipment with a microchip.

Semi-mobile Stingray rogue field intercept cell tower antenna array with collection/detection gear powered by a grid utility pole with a backup battery, photographed by drone near to where Standing Rock Chairman was arrested – photo by Myron Dewey
Only government entities can authorize a cyber or cellular attack.
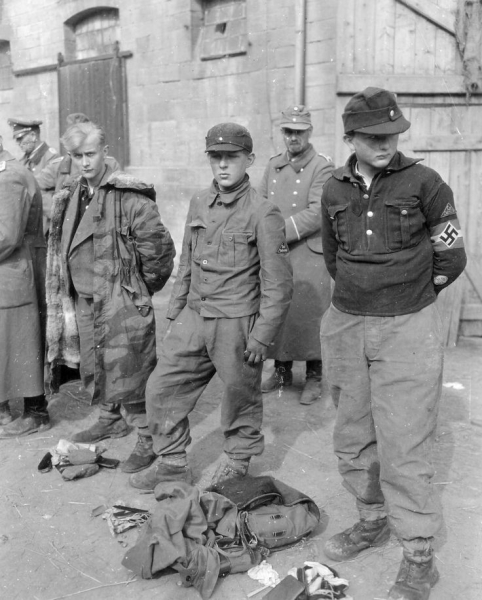
Plucked from the war-torn fields of Afghanistan and Iraq, TigerSwan employees are well trained in military tactics, and the company not only advertises its military-grade data and human intelligence capabilities on its website, it has a history of partnering with hi-tech companies, such as its 2012 partnership with Saffron Technology.
Saffron Technology is a small data analytics company that uses technology to mimic the human brain’s capability to connect people, places, and things, at lightning speed, according to the company’s website. Saffron Technology’s products were originally used in Iraq to predict where bombs were located, according to Reuters, but now it offers its services to corporations such as Boeing Co., to forecast weather, and to TigerSwan.
While IT technicians continue the hunt for additional proof of cyber weaponry used at the Standing Rock camps, the Water Protector Legal Collective, which operates in partnership with the National Lawyers Guild in defending many activists, reports Kourtni Dockter, a former DAPL security employee, is not the only whistleblower.
On Tuesday night, Kyle Thompson, the former project manager for Leighton Security Security Services, came forward live on Digital Smoke Signals with owner Myron Dewey, and began to tell his side of the Dakota Access Pipeline story, making hints that more is to come. Thompson’s burgeoning testimony comes after his former girlfriend and Leighton security employee, Dockter, blew the whistle on TigerSwan activities.
“We are starting to see some of the security workers defect,” Water Protector Legal Collective staff attorney Andrea Carter said. “When you look at Kyle’s interview yesterday, i think he feels very troubled about what happened, and a part of him really wants to connect to the camps.”
Thompson plans on sharing more information about his experience working security along the Dakota Access Pipeline, but “not yet,” he said.
“I feel like I can help a lot of people with me coming out with my truth, which could benefit the people facing charges,” Thompson said during the recorded interview.
“The healing has started,” Dewey said. “And it’s not easy.”
The casualties
As the Dodge Ram’s engine sputtered, Alex Glover-Herzog wasn’t thinking of the military-Internet complex or of TigerSwan, or of the DAPL helicopter that swooped low along the Missouri River’s banks.
Late November outside of Standing Rock, Glover-Herzog was trying to stay warm. His 4×4’s engine was purring normally, pouring much-needed heat from the vents before the engine coughed, then suddenly died.
“It was way too cold to think about anything else at that moment,” Glover-Herzog said. “The only thing I can say is that my truck died twice for no reason while at Oceti.”
Hundreds of others camped outside of Standing Rock during the Dakota Access Pipeline controversy experienced the same phenomena, Myron Dewey, owner of Digital Smoke Signals, said. It resembled a futuristic nightmare straight from the movie “Matrix,” executive director for Geeks Without Bounds, Lisha Sterling, said. She spent months at the camps training people and helping improve communication technology. Geeks Without Bounds is a Washington-based humanitarian organization that works toward improving communication and technology.

Two automobiles that suddenly lost battery power at Standing Rock camps – photo provided by Myron Dewey
“When the squids were coming at them.” Sterling said about the comparison of the “Matrix” scene and what happened at the Standing Rock camps. “They powered down their machine and did an EM pulse, which fries electronics… and the squids coming at them.”
Cooper Quentin, the staff technologist on the cyber team with Electronic Frontier Foundation, a nonprofit organization defending liberties in the digital world, spent a few days at the Standing Rock camps.
“While I was there I was looking for evidence of Stingrays, and I did not find any evidence,” Quentin said. “But they could have been using them before I got there.”
He looked at computers, mobile phones, but said he found nothing conclusive.
“There is definitely some weird stuff, and I don’t think it’s a coincidence, but it doesn’t have to be malware. Extreme temperatures can do weird things to phone batteries. There were definitely a lot of weird things going on at the camps, but none of that is exclusive.”
Quentin is still interested in investigating further, however, but the case needs a digital forensics expert, which is costly.
“Even if we do find malware that looked like spyware, and we were able to prove from time stamps that they got it while they were at Standing Rock, we would still need to prove where it came from. If the server is owned by law enforcement or TigerSwan, then you have solid attribution. If that’s not the case then it becomes much harder to figure out who to blame.
“But my opinion is not shared by some of the other experts. If people have solid evidence I would happily continue to investigate.”
Colorado resident Christina Arreguin’s first phone at Standing Rock became little better than a paperweight in mid-October, she said. She had 80 percent battery left when it got hit, but even after trying three separate chargers, her phone was never able to call or text again. She learned to adapt quickly; stowed the battery in one pocket, and her new phone in the other when she went to the frontlines.
The attacks weren’t isolated to the frontlines. Cars broke down when a helicopter flew by, she noticed.
“The sound from the planes so much became like part of the background, just a familiar noise, kinda like how you get used to the beep from a smoke detector after a while,” Arreguin said. “I do remember a helicopter though, when the Blazer broke down it looked different than the other ones.”
“When the Cessna flew by, that’s when cellphones got zapped,” Lisa Ling, also with Geeks Without Bounds, said. Ling is a former Air Force technical sergeant who worked in America’s armed drone program in what is known as a Distributed Ground System, a secret networked killing operation capable of sucking up personal data to be able to track and shoot people anywhere, and at any time. Ling turned whistleblower in 2014, and her testimony was featured in the 2016 documentary film National Bird.
On Ling’s first trip to the Standing Rock camps, Internet connection was difficult.
“When we first got there the only place you could get any connectivity was Facebook Hill,” Ling said. “If you left Facebook Hill there was no connectivity.” On her second trip, she said random places in the camps had connectivity. She knocked on tent and tipi doors asking people if they had boosters. No one had any.
“My phone actually got zapped a number of times by some sort of EMP,” Ling said. “These cellular disruptors, as we call them, can do physical damage to the phone.” Such an attack is not legal for a private company to issue, and Ling said it should not be legal for law enforcement to utilize without warrants.
FOIA requests to the Office of the Governor of North Dakota, to the Bureau of Indian Affairs, to the North Dakota National Guard, so far, have revealed that no warrants were issued for the use of cyber weapons outside of Standing Rock.
Such attacks are an invasion of privacy, a right protected by the Fourth Amendment of the US Constitution, which states: “The right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers, and effects, against unreasonable searches and seizures, shall not be violated, and no warrants shall issue, but upon probable cause.”
“I paid close attention to what things flying above us when certain things happened,” Ling said. “And there was a small white plane, and that’s the thing that flew when our phones got zapped. So if you managed to turn your phone off when that thing came by, then your phone wouldn’t get zapped. When that Cessna was up, cellphones got zapped, and it wasn’t because of the cold, as they’re trying to say, it happened before the winter as well.”
Ling brought radios to the camps to help with communication and safety during sub-zero temperatures, she said, but TigerSwan operatives discovered their frequencies and harassed them. Internet cables were cut inside the dome by infiltrators, she said.
“They were intentionally interrupting that,” Ling said, adding that during the freezing winter months such interruptions could have cost lives.
The automobile breakdowns coincided with either the private Cessna that circled the camps, or with helicopters.
“I documented, I have proof,” Dewey said. Proof was easy to obtain because of the “digital divide” separating Indian country and the rest of the modernized world. He spotted and photographed a Stingray device near Highway 1806 where Standing Rock Sioux Tribe Chairman Dave Archambault II was arrested.
The device has been identified by multiple sources as a semi-mobile Stingray rogue field intercept cell tower antenna array with collection and detection gear powered by a grid utility pole with a battery backup.
“It was easy to identify cyber warfare out there, because we already were in a digital divide,” Dewey said. Dewey is also a filmmaker, uses drones, and lost at least three to gunfire and electromagnetic field devices, he said. Charges against Dewey were dropped this week, and he is waiting the return of one of his drones in Mandan.
“Indian country has been in a digital divide since America has had access to technology.”
Dewey claims that TigerSwan operatives on snowmobiles chased him while he was driving, and he has video to prove the harassment. One of his drones was hit at Treaty Camp, which was taken over by law enforcement on October 27, 2016.
“The drones were hit several different ways, so I sent one drone up and another to film it and see what happened,” Dewey said. “It seemed like an EMP charge, but it was more like a wave, and it dropped into the water.”
His mobile phone also got hacked, Dewey said. “It started recording my voice right in front of me and another guy, and then sent to text. I was really paranoid a lot of the times, but I had people to protect me some times.”
In addition to the cyber attacks, TigerSwan operatives, or security personnel working under the TigerSwan umbrella, boarded vehicles like pirates to a ship, he said, smashed out windows, stole radios to report misleading information, and curse.
“‘We’re going to rape your women and have half-breed babies,’” Dewey said the security operatives would yell over frequencies activists used. The threats were difficult to ignore as they brought on old fears from native oral stories and traditions handed down for generations.
“If the military catches you, stuff your insides with dirt in the hopes that they kill you,” Dewey said. “We thought the police were there to keep the peace, but it was like Custer who wanted the gold. History repeating itself, the second wave of Custer’s cavalry, and they felt the need to win.”
Dewey drives a Yukon Hybrid, and had just installed a new battery when it too was fried at the Standing Rock camps. The first electromagnetic pulse hit the camps in August, Dewey said. “Several hoods were up, and I went over and asked them what happened and they said they’re batteries were dead as well.”
The cyber field of battle sits in a legal gray zone, but inside the United States only a government entity has the authority to utilize use cyber weapons. Private companies, even if they are attacked first, cannot legally reciprocate on their own volition.
“So my educated guess is that the IMSI Catchers were owned and authorized by either or both the Morton County Sheriff’s Department and the National Guard, but the chances are similarly high that they would not have had the experience to manage them, so that is where TigerSwan comes in,” Sterling said.
“It is also possible that nobody really cared, and that they were owned by TigerSwan themselves.”
Outside of the NSA, the CIA, the FBI, and a handful of other government agencies, only criminal organizations and massive corporations have the funds to purchase and store high-end disruptive cyber weapons. A zero-day vulnerability exploit targeting Apple products can cost as much as $500,000.
IMSI Catchers used to be difficult to obtain, but now can be bought online for under $2,000 on Alibaba, or from dozens of companies online some of whom specify their products are for law enforcement use only.
“What we got now is the lull between battles,” Sterling said. “It will more likely be seen in the big cities soon, Standing Rock Part Two, in terms of the cyber warfare, the strong-armed tactics, and not just militarized police, but the militarized contractors as well.”
The gray zone
Cyber weapons are not lethal in the sense of traditional weapons, but can also be dangerous and disruptive far beyond an intended target, Shane Harris, the author of the 2014 book “@ War: The Rise of the Military-Internet Complex,” wrote. Harris is a senior correspondent at the Daily Beast and covers national security, intelligence, and cyber security.
Cyber warfare began in the 1990s. Early pioneers, or cyber warriors, blazed a complicated legal trail into the 2000s until 2013, when former President Barack Obama issued executive order PDD-20, effectively paving the way for more streamlined cyber defense and offense.
The president must order all cyber strikes internationally; no private companies are authorized for digital, cellular, or cyber offensive actions. Despite a contentious relationship between government agencies and private companies, “there’s an alliance forming between government and business in cyberspace,” Harris wrote.
“It’s born of a mutual understanding that US national security and economic well-being are fundamentally threatened by rampant cyber espionage and potential attacks on vital infrastructure,” Harris wrote.
Oil pipelines are included under the infrastructure category by the Department of Homeland Security, as are dams, chemicals, emergency services, communications, critical manufacturing, healthcare, water and wastewater, transportation, information technology, and government facilities, along with other sectors of economy.
Approximately 85 percent of the computer networks in the United States are owned and operated by private groups and individuals, and any one of the telecom companies, the tech titans, the financial institutions, the defense contractors, could be the weak link against cyber attacks.
“The government has decided that protecting cyberspace is a top national priority,” Harris wrote. “But the companies have a voice in how that job gets done. That’s the alliance at the heart of the military-Internet complex.”
The Homeland Security Presidential Directive, or HSPD-7, signed by former president George W. Bush on December 17, 2003, seeks to protect infrastructure from “terrorist attacks.”
During the months TigerSwan was illegally involved as the chief security organizer for Energy Transfer Partners’s oil interests, the security company called activists camped against the Dakota Access Pipeline terrorists, even jihadists.
“Terrorists seek to destroy, incapacitate, or exploit critical infrastructure and key resources across the United States to threaten national security, cause mass casualties, weaken our economy, and damage public morale and confidence,” HSPD-7 reports.
“While it is not possible to protect or eliminate the vulnerability of all critical infrastructure and key resources throughout the country, strategic improvements in security can make it more difficult for attacks to succeed and can lessen the impact of attacks that may occur. In addition to strategic security enhancements, tactical security improvements can be rapidly implemented to deter, mitigate, or neutralize potential attacks.”
The lines between spies, saboteurs, or intelligence gathering and military operations are blurred. Intelligence gathering techniques fall into a legal gray area and while the tactic may not be illegal for a federal or police agency to conduct on US citizens, the evidence obtained by such means may still not be allowed in a court of law.
Daily, TigerSwan coordinated and provided intelligence to Energy Transfer Partners and others. TigerSwan placed operatives in the law enforcement joint operations center, and were responsible for in-depth analyses of cyber, workforce, facility, electronic, and environmental security threats, according to the North Dakota Private Investigation and Security Board.
Emails shared between Morton County Sheriff’s Department Public Information Officer Rob Keller and Office of the Governor of North Dakota Communications Director Mike Nowatzki, the governor’s office was knowledgeable of TigerSwan’s activity, but reported they did not know the security company was working illegally.
“I wanted to give you a heads up on this Energy Transfer and TigerSwan meeting with Kyle [Kirchmeier],” Keller wrote to Nowatzki on January 16. “I don’t know the intent and the PIOs will not be there.”
“If it is a closed session, it’s fine,…” Nowatzki wrote back. “Our JIC PIO and Unified Command meet from 0830 to 1000 (CT) every Tuesday so that battle rhythm should be protected with our state team.”
Battle rhythm is a military term, meant to describe the maintenance of synchronized activity and process among distributed “warfighters,” according to the Defense Technical Information Center.
“I was deployed to the Middle East, and the term was used there,” Ling said. “I worked in the drone program, and the term was there. I worked in the National Guard and the term was used there, but I have never heard the term battle rhythm used in a civilian setting. It would imply that there is an enemy.”
– This story is part of the ongoing investigation into government and TigerSwan’s actions during the Dakota Access Pipeline controversy.